Tiny Homes on Foundations: Plans and Considerations
The tiny home movement has gained significant momentum in recent years, appealing to individuals seeking financial freedom, minimalist lifestyles, and reduced environmental impact. While many envision tiny homes as mobile structures, a significant proportion are choosing to build these compact dwellings on permanent foundations. This approach offers a blend of the benefits of a tiny home with the stability and permanence associated with traditional housing. This article will explore the crucial aspects of tiny home on foundation plans, outlining the necessary considerations, available resources, and potential challenges associated with this building endeavor.
The decision to build a tiny home on a foundation involves a variety of factors that differentiate it from constructing a tiny home on wheels. These factors include adherence to local building codes, zoning regulations, and the acquisition of necessary permits. Planning is paramount, and selecting the correct plans that meet both personal needs and regulatory requirements is a critical first step.
Understanding Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
Before embarking on any construction project, a thorough understanding of local regulations is essential. This is particularly pertinent when considering a tiny home on a foundation, as these structures often fall into a grey area within established building codes. Many municipalities have specific minimum square footage requirements for permanent residences, which can present a challenge when building a tiny home. Therefore, one must investigate the following:
Zoning Regulations: Zoning regulations dictate how land can be used within a specific area. These regulations may impose restrictions on the size, location, and type of structures permitted on a particular plot. Researching the local zoning ordinances will determine if a tiny home on a foundation is allowed and if any specific conditions must be met.
Building Codes: Building codes are standardized sets of rules and guidelines that ensure the safety and structural integrity of buildings. Tiny homes on foundations must comply with the applicable building codes, which may vary depending on the location. These codes address aspects such as foundation requirements, structural integrity, electrical wiring, plumbing, and fire safety.
Permitting Process: The permitting process involves submitting building plans and documentation to the local authorities for review and approval. Obtaining the necessary permits is crucial to ensure that the construction project is legal and compliant with all applicable regulations. The permitting process may involve inspections at various stages of construction to verify compliance with the approved plans and building codes.
Securing the correct permits can be a lengthy and potentially complicated process. It's advisable to consult with local building officials or experienced contractors familiar with tiny home construction to navigate the regulatory landscape effectively. Failing to comply with local regulations can result in fines, delays, or even the need to demolish the structure.
Evaluating Tiny Home on Foundation Plans
Once the legal and regulatory frameworks are understood, the next step is to evaluate the available tiny home on foundation plans. These plans serve as the architectural blueprint for the construction project, outlining the dimensions, layout, and structural details of the home. A well-designed plan is crucial for ensuring that the tiny home is structurally sound, functional, and aesthetically pleasing.
There are several options for obtaining tiny home on foundation plans:
Pre-Designed Plans: Many companies specialize in creating pre-designed tiny home plans that can be purchased online or through architectural firms. These plans offer a convenient and cost-effective option for individuals who prefer a pre-existing design. When selecting pre-designed plans, it is essential to ensure that they meet local building codes and zoning regulations. These must also align with personal preferences, such as the number of rooms, the type of foundation, and aesthetic style.
Custom-Designed Plans: For individuals who have specific design requirements or preferences, custom-designed plans may be the most suitable option. Custom plans involve working with an architect or designer to create a unique plan that meets the individual's specific needs and desires. Although custom plans are more expensive than pre-designed plans, they offer greater flexibility and the ability to tailor the design to the specific site and regulatory requirements.
DIY Plans: For those with experience in construction and design, DIY plans may be a viable option. However, creating DIY plans requires a thorough understanding of building codes, structural engineering principles, and architectural design. It also requires significant time and effort to develop detailed and accurate plans. This option should only be considered by individuals with the necessary skills and expertise.
Regardless of the chosen option, several essential elements must be present in the plans:
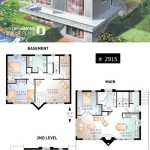
Detailed Floor Plans: Detailed floor plans should clearly indicate the dimensions of each room, the location of doors and windows, and the placement of appliances and fixtures. They should provide an overview of the living space and ensure that the layout is functional and efficient.
Foundation Plans: Foundation plans provide detailed information about the foundation system, including the type of foundation (slab, crawl space, or basement), the dimensions of the foundation walls, and the type of materials used. The foundation plans must be designed to withstand the local soil conditions and the weight of the structure.
Elevation Drawings: Elevation drawings depict the exterior of the tiny home from various angles. These drawings show the roofline, window placement, siding materials, and other architectural details. They help to visualize the finished product and ensure that the design is aesthetically pleasing.
Structural Details: Structural details provide information about the structural components of the tiny home, such as the framing system, roof trusses, and load-bearing walls. These details are essential for ensuring that the structure is structurally sound and can withstand wind, snow, and seismic loads. Consulting with a structural engineer is highly recommended to ensure the structural integrity of the design.
Material List: A comprehensive material list outlines all the materials needed for the construction project, including lumber, siding, roofing, windows, doors, and fixtures. The material list should specify the quantity, size, and type of each material, making it easier to estimate costs and purchase supplies.
Foundation Options and Construction Considerations
The foundation is the base upon which the tiny home rests, and its design and construction are critical for the stability and longevity of the structure. Several foundation options are available for tiny homes, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of foundation will depend on factors such as the local soil conditions, building codes, budget, and personal preferences.
Slab Foundation: A slab foundation is a concrete slab poured directly onto the ground. This type of foundation is relatively inexpensive and easy to construct, making it a popular choice for tiny homes. Slab foundations are suitable for sites with stable soil conditions and good drainage. However, slab foundations do not provide access to plumbing and electrical systems, which can make repairs and modifications more challenging.
Crawl Space Foundation: A crawl space foundation is a raised foundation that creates a shallow space between the ground and the floor of the tiny home. This type of foundation provides access to plumbing and electrical systems, making it easier to perform repairs and modifications. Crawl space foundations also offer some protection against moisture and pests. However, crawl space foundations are more expensive to construct than slab foundations and require proper ventilation to prevent moisture buildup.
Basement Foundation: A basement foundation is a fully excavated foundation that creates a usable space beneath the tiny home. Basement foundations provide additional living space, storage space, or a mechanical room. They also offer excellent protection against moisture and pests. However, basement foundations are the most expensive type of foundation to construct and require significant excavation and reinforcement. They are also subject to specific building codes related to water-proofing and egress requirements.
Regardless of the chosen foundation option, several construction considerations are essential:
Soil Testing: Before constructing any foundation, it is crucial to conduct soil testing to determine the soil's load-bearing capacity and drainage characteristics. Soil testing will help to ensure that the foundation is designed to withstand the local soil conditions and prevent settling or cracking.
Drainage: Proper drainage is essential to prevent water from accumulating around the foundation, which can lead to moisture damage and structural problems. Installing a drainage system, such as a French drain, can help to divert water away from the foundation.
Insulation: Insulating the foundation can help to improve energy efficiency and prevent heat loss. Foundation insulation can be applied to the exterior or interior of the foundation walls.
Waterproofing: Waterproofing the foundation is essential to prevent moisture from penetrating the foundation walls and causing damage to the interior of the tiny home. Waterproofing can be achieved by applying a waterproof membrane to the exterior of the foundation walls.
Constructing a tiny home on a foundation is a complex undertaking that requires careful planning, attention to detail, and compliance with local regulations. Selecting the appropriate plans, understanding the regulatory frameworks, and choosing the right foundation are crucial steps for ensuring the success of the project. By investing the time and effort required to properly plan and execute the construction, individuals can create a sustainable, affordable, and aesthetically pleasing tiny home that meets their specific needs and desires.

Free Foundation Plan For 16 Wide Little House Project

New Minim House Plan Set Homes

Tiny House Foundation Types Of Foundations Construction Concrete Slab

Tiny House Plans On A Foundation Tumbleweed Houses

Teacup Tiny Homes S On Foundation

I M Building A Not So Tiny House Part 1 Permits Site Prep Crafted Work

Perfect House Plans For A Pile Foundation Dfd Blog

1 Bed Tiny House Plan With Fireplace 22129sl Architectural Designs Plans

Tiny House Plans On A Foundation Tumbleweed Houses

16 Cutest Tiny Home Plans With Cost To Build Craft Mart