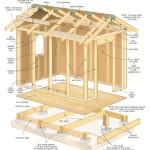
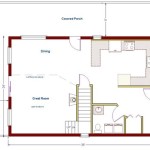
Barndominium Floor Plans: Incorporating a Safe Room for Enhanced Security
Barndominiums, a portmanteau of "barn" and "condominium," represent a growing trend in residential construction. They offer a unique blend of rustic charm, open space, and cost-effectiveness, often constructed from repurposed agricultural buildings or utilizing metal building kits. As barndominium popularity increases, so does the interest in integrating modern safety features, most notably a safe room.
A safe room, also known as a panic room, is a hardened structure designed to provide near-absolute protection during extreme weather events, home invasions, or other emergency situations. Integrating a safe room into a barndominium floor plan requires careful consideration of several factors, including location, construction materials, size, and accessibility. This article will explore the key considerations for incorporating a safe room into a barndominium design, emphasizing safety, functionality, and compliance with relevant building codes.
Key Point 1: Planning and Location of the Safe Room
The initial phase of incorporating a safe room involves meticulous planning. The location of the safe room is paramount and should be selected strategically to maximize its accessibility and effectiveness. An interior location, ideally on the ground floor, is generally preferred, offering easier access during emergencies, particularly for individuals with mobility limitations. Avoid exterior walls if possible, as they are more susceptible to damage during extreme weather.
Proximity to bedrooms is a considerable advantage, allowing occupants to reach the safe room quickly during nighttime emergencies. Consider the potential for debris blockage following a catastrophic event when choosing the location. The safe room should be readily accessible and not easily obstructed by collapsed structures or fallen trees. Furthermore, ensure the location is away from potential fire hazards, such as the kitchen or areas with flammable materials.
Accessibility considerations extend beyond the immediate proximity. The path leading to the safe room must be clear and well-lit, even during power outages. Wide corridors and easily navigable routes are crucial, especially if occupants may be disoriented or panicked. Consider incorporating features like glow-in-the-dark markers or emergency lighting along the path. The internal layout of the barndominium should facilitate a rapid and safe retreat to the designated safe zone.
The size of the safe room is another crucial planning factor. The dimensions should be sufficient to accommodate all expected occupants comfortably for an extended period. Consider the average number of people residing in the barndominium, as well as any potential guests or family members who might seek refuge during an emergency. Allow for ample space for seating, supplies, and movement. A cramped safe room can lead to discomfort and anxiety, potentially hindering its effectiveness.
The room's planned use will dictate features required. Will the safe room serve solely as a refuge during emergencies, or will it also function as a storage space or a home office? If the latter, integrating shelving, desks, and power outlets might be appropriate, but it is extremely important to ensure the primary function as a safe harbor isn’t compromised. Carefully delineate between essential safety supplies and non-essential items.
Key Point 2: Construction Materials and Structural Integrity
The structural integrity of the safe room is the most critical aspect of its design and construction. The materials used must be capable of withstanding extreme forces, including high winds, projectiles, and forced entry. Reinforced concrete is generally considered the gold standard for safe room construction, offering superior protection against a wide range of threats.
Walls should be constructed of solid concrete, poured-in-place or pre-cast, with a minimum thickness of eight inches. Alternatively, concrete masonry units (CMUs) can be used, but they must be reinforced with steel rebar and filled with concrete. Regardless of the method, ensure the walls are securely anchored to the foundation and roof to prevent separation during extreme events.
The roof of the safe room must be equally robust. A reinforced concrete roof is ideal, but if the existing barndominium structure has a different roof type, additional reinforcing measures are necessary. These measures may include adding steel plating or additional layers of structural sheathing. The roof must be able to withstand significant impact from falling debris, such as tree limbs or roofing materials.
The door to the safe room is a particularly vulnerable point. It must be a heavy-duty, impact-resistant door designed specifically for safe room applications. These doors typically feature solid steel construction, multiple locking points, and reinforced frames. Ensure the door swings inward to prevent it from being blocked by debris outside. The hinges and locking mechanisms must be robust and tamper-proof.
Ventilation is another critical consideration. The safe room must have a source of fresh air to ensure occupants can breathe comfortably for an extended period. An independent ventilation system, such as a manually operated fan or a filtered air intake, is essential. This system should be protected from external contaminants and should be capable of providing adequate airflow for the number of occupants. Consider including a carbon monoxide detector to monitor air quality within the safe room.
Penetrations through the walls of the safe room, such as for electrical wiring or plumbing, should be carefully sealed to maintain the structural integrity of the walls. Use non-shrink grout or other appropriate sealant to fill any gaps around conduits or pipes. The goal is to create a continuous, monolithic structure that is resistant to breaches.
Key Point 3: Essential Supplies and Emergency Preparedness
A well-equipped safe room is essential for ensuring the comfort and safety of occupants during an emergency. The supplies stored inside should be sufficient to meet the basic needs of all occupants for an extended period, typically a minimum of 72 hours. This includes food, water, first-aid supplies, communication devices, and sanitation equipment.
Water is a fundamental necessity. Store a supply of bottled water or a water purification system within the safe room. The amount of water needed will depend on the number of occupants and the anticipated duration of the emergency. A general guideline is to store at least one gallon of water per person per day. Additionally, consider storing water purification tablets or a portable water filter as a backup.
Non-perishable food items are also essential. Choose foods that are easy to store, require no cooking, and have a long shelf life. Examples include canned goods, protein bars, dried fruits, and nuts. Consider the dietary needs of all occupants, including children, seniors, and individuals with medical conditions.
A comprehensive first-aid kit is crucial for addressing injuries or medical emergencies. The kit should include bandages, antiseptic wipes, pain relievers, gauze pads, adhesive tape, and any personal medications required by occupants. It is advisable to include a first-aid manual and to ensure that at least one occupant is trained in basic first-aid procedures.
Communication devices are essential for contacting emergency services or staying informed about the situation outside. A battery-powered or hand-crank radio can provide updates on weather conditions or emergency broadcasts. A fully charged mobile phone or satellite phone can be used to call for help, but it is important to conserve battery power. A whistle can be used to signal for help if occupants are trapped or injured.
Sanitation is often overlooked but is crucial for maintaining hygiene and preventing the spread of disease during an extended stay in the safe room. A portable toilet or sanitation kit is highly recommended. Include toilet paper, hand sanitizer, and garbage bags. Proper waste disposal is essential for maintaining a sanitary environment.
Other essential supplies include flashlights with extra batteries, blankets or sleeping bags, a crowbar for prying open doors or windows, and personal hygiene items. A copy of important documents, such as insurance policies and identification, should also be stored in the safe room.
Regular maintenance and inspection of the safe room and its contents are crucial. Check the stored food and water for expiration dates and replace as needed. Inspect the ventilation system to ensure it is functioning properly. Test the communication devices and replace batteries regularly. Practice drills with all occupants to ensure they know how to access the safe room and what to do in an emergency.
Finally, it's important to consult with local building codes and regulations to ensure the safe room meets all applicable standards. Compliance with these codes is essential for ensuring the safety and effectiveness of the safe room. Professional design and construction are highly recommended to ensure the safe room is built to withstand the forces it is intended to resist.

1 Story Barndominium House Plan With Safe Room 2758 Sq Ft 623116dj Architectural Designs Plans

Beautiful Barndo House Plans Blog Eplans Com

Best Open Concept Barndominium Floor Plans That Maximize Space And Functionality Pole Barn House Metal

2 Story Barndominium House Plan

Barndominium House Plans With Safe Room

Top 20 Barndominium Floor Plans That You Will Love

Top 20 Barndominium Floor Plans That You Will Love

Barndominium House Plan Model 4254

Pin Page

One Level Hill Country House Plan With Safe Room 48600fm Architectural Designs Plans