Narrow 4 Bedroom House Plans: Maximizing Space on Restricted Lots
Narrow lot homes present a unique architectural challenge: how to create a comfortable and functional living space within restrictive width dimensions. Designing a four-bedroom house plan for a narrow lot requires meticulous planning, innovative design solutions and a keen understanding of spatial optimization. These plans must effectively utilize vertical space, prioritize natural light, and minimize wasted areas to create a home that feels spacious and inviting, despite its limited footprint. This article explores key considerations in narrow 4-bedroom house plans, highlighting strategies for maximizing space and comfort while adhering to lot constraints.
Understanding the Constraints of a Narrow Lot
The primary constraint in designing for a narrow lot is, of course, width. Lot widths considered “narrow” commonly range from 25 to 50 feet. This limitation impacts several aspects of the home's design, including the placement of rooms, circulation patterns, and access to natural light. Traditional, sprawling floor plans are impractical in these scenarios, necessitating a shift toward vertical development and strategic space allocation. Setback requirements imposed by local zoning regulations further restrict the buildable area, potentially impacting the overall size and shape of the house. Parking considerations, such as garage placement or driveway access, also play a crucial role in optimizing the narrow lot's space. A carefully considered plan will consider all these limitations upfront to produce a viable design.
Beyond the physical limitations of the lot, cost considerations are also relevant. Building upwards generally increases the overall construction budget due to the need for stronger structural support and potentially more complex foundation work. Material selection also plays a role in maximizing the project’s budget, and minimizing waste is essential to controlling expenses. The building design must also consider the access points onto the property during construction. Narrow lots can often present construction access challenges that may significantly increase project costs.
Finally, an important consideration for narrow lots is the local building codes and homeowners association regulations. These codes often dictate maximum building height, setback requirements, allowable building materials, and the design aesthetic allowed within the community. Ignoring these requirements can result in significant delays, costly revisions, and even legal issues. Before finalizing any design, it’s critical to research and understand all applicable regulations to ensure the design complies and is ultimately buildable. Engaging a local architect or builder familiar with the area's regulations is often a worthwhile investment.
Key Design Strategies for Maximizing Space
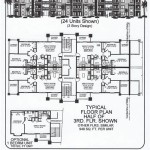
Several design strategies can effectively maximize space in narrow 4-bedroom house plans. One common approach is vertical development, which focuses on building upwards to increase the total floor area. Multi-story designs allow for more bedrooms and living spaces without expanding the building's footprint. This approach often incorporates efficient staircase designs to minimize their impact on usable floor space.
Open-concept layouts are another popular strategy for creating a sense of spaciousness. Removing walls between the kitchen, living, and dining areas creates a larger, more unified space that feels less confined. This design also promotes better natural light distribution throughout the home. Thoughtfully placed windows and skylights are crucial for maximizing natural light penetration in narrow homes, which may have limited access to sunlight due to adjacent buildings or landscaping.
Storage solutions are particularly important in narrow homes where space is at a premium. Built-in shelving, under-stair storage, and multi-functional furniture can help maximize storage capacity without sacrificing living space. In addition, the design can integrate flexible spaces that can serve multiple purposes. A guest bedroom could double as a home office, or a living room could easily convert into a home theater.
Another key consideration is the flow of traffic within the house. Well-planned circulation paths ensure that movement is efficient and doesn't interfere with the functionality of the rooms. Minimizing hallways and dead spaces can significantly increase the usable floor area. The use of strategically placed mirrors can also create the illusion of greater space and enhance the sense of openness. Finally, the careful selection of furniture and décor can significantly impact the overall feel of a narrow home. Opting for smaller-scale furniture and minimalist décor can prevent the space from feeling cluttered or cramped.
Structural and Architectural Considerations
The structural design of a narrow home requires careful attention to ensure stability and safety. Given the vertical nature of these designs, the foundation and framing must be robust enough to support multiple stories. Structural engineers play a vital role in determining the appropriate materials and construction techniques to meet these requirements. Party walls, shared with neighboring properties, may also require specific structural considerations and adherence to local building codes.
From an architectural point of view, the exterior design should complement the surrounding neighborhood while maximizing the house's curb appeal. Limited width can present challenges in terms of visual balance and proportion; however, creative use of windows, siding materials, and architectural details can enhance the home's aesthetic appeal. A well-designed façade can make a narrow house appear wider and more inviting.
Consideration of the building materials plays a critical role. Light-weight materials can reduce the load on the structure, potentially reducing foundation costs. Durable and low-maintenance materials are also ideal for narrow lots, given the limited access for repairs and maintenance. It is also important to consider the environmental impact of the selected materials, as well as their ability to contribute to energy efficiency. Proper insulation is particularly crucial in narrow homes, as it can help reduce heating and cooling costs and improve the home's overall comfort.
Green building practices can be incorporated into the design to enhance the home's sustainability and reduce its environmental footprint. Solar panels, rainwater harvesting systems, and energy-efficient appliances can significantly reduce the home's reliance on external resources. Additionally, landscaping can play a role in improving the property's aesthetics, providing shade to keep the house cooler, and minimizing storm water runoff. The design should also take into account the orientation of the house to maximize solar gain in the winter and minimize it in the summer. In addition, proper ventilation design is important to maintaining healthy air quality within the home and further reduce the need to use the HVAC system.
Floor Plan Organization: Bedrooms, Bathrooms, and Living Areas
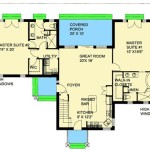
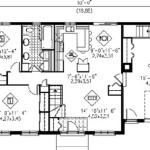
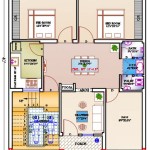
Organizing the floor plan of a narrow 4-bedroom house requires strategic consideration of room placement and functionality. One common approach is to locate the bedrooms on the upper floors to maximize privacy and separation from the main living areas. The master bedroom typically occupies the most desirable location, often at the rear of the upper floor, away from street noise. The other three bedrooms can be arranged to optimize space and minimize hallway length. Shared bathrooms or en-suite bathrooms can be incorporated to serve the bedrooms. Careful planning of door placement is important in order to minimize the amount of space wasted on the swing radius of the door.
The main living areas, including the kitchen, living room, and dining area, are typically located on the ground floor. An open-concept layout is ideal for creating a spacious and inviting atmosphere. The kitchen should be efficiently designed with ample counter space and storage. The living room should be arranged to maximize seating and natural light. The dining area should be positioned to facilitate easy access from both the kitchen and the living room.
Basements, if present, can be utilized for additional living space, storage, or recreational areas. A finished basement can significantly increase the usable floor area of a narrow home. If a basement is not feasible due to lot conditions or budget constraints, the garage can be incorporated into the main floor plan. Attached garages can provide convenient access to the house and additional storage space. Detached garages can be an option if setback requirements allow. Finally, outdoor spaces, such as decks, patios, or balconies, can extend the living area beyond the confines of the house. These spaces should be designed to maximize usability and privacy while complementing the overall architectural style of the home.

Pin Page

4 Bedroom Small Plot Home Design With Free Plan

Farmhouse Style House Plan 4 Beds 3 5 Baths 2001 Sq Ft 430 243

Anvard Luxury Narrow Lot Villa Sater Design Collection House Plans

Morning Star Farm House Plan Narrow Archival Designs

N Houses Small Land House Plan Narrow Lot 4 Bedroom New Design

Plan 42026mj Narrow New American Cottage House With 3 Or 4 Beds

House Plan 76605 Narrow Lot Style With 2163 Sq Ft 4 Bed 2 Bat

Floor Plan Ideas For Diffe Areas

Vitality House Plan Two Story Narrow Lot Home Design Mm 1869 A