Sample Floor Plans With Dimensions: A Comprehensive Guide
Floor plans with dimensions serve as fundamental tools in architecture, interior design, real estate, and construction. They provide a scaled representation of a room, building, or property, including the length, width, and height of various elements. These plans are essential for understanding the layout, spatial relationships, and overall functionality of a space. This article delves into different types of sample floor plans with dimensions, highlighting their features, benefits, and applications across various fields.
Understanding the Importance of Dimensional Accuracy
The accuracy of dimensions in a floor plan is paramount. Errors, even small ones, can lead to significant problems during construction, renovation, or furniture arrangement. Accurate dimensions ensure that materials are ordered correctly, spaces are utilized efficiently, and building codes are met. Furthermore, precise dimensions are crucial for creating realistic 3D models and virtual tours, allowing stakeholders to visualize the finished product before physical construction begins.
Dimensional accuracy extends beyond just the length and width of rooms. It includes the placement and size of windows, doors, walls, fixtures, and other permanent features. Building Information Modeling (BIM) software often incorporates dimensional data, allowing for clash detection and ensuring that different building systems (e.g., plumbing, electrical, HVAC) are coordinated effectively. Dimensional accuracy also facilitates cost estimation, as precise measurements allow for accurate calculations of material quantities and labor costs.
Different scales are used in floor plans, depending on the size and complexity of the project. Common scales include 1/4 inch = 1 foot and 1/8 inch = 1 foot. The chosen scale should be clearly indicated on the plan. It is also important to distinguish between interior and exterior dimensions. Exterior dimensions typically refer to the overall size of the building, while interior dimensions represent the size of rooms and spaces within the building's envelope.
Types of Floor Plans and Their Dimensional Representations
Floor plans can be categorized based on their purpose and the level of detail they provide. Several common types are outlined below:
*Conceptual Floor Plans:
These plans offer a preliminary overview of the layout, focusing on the general arrangement of rooms and spaces. Dimensions are often approximate and may not include fine details. They are used primarily for initial space planning and brainstorming. *Detailed Floor Plans:
These plans provide precise dimensions for all walls, doors, windows, fixtures, and other elements. They are used for construction documents, permit applications, and interior design purposes. Detailed floor plans also include notations on materials, finishes, and construction methods. *Furniture Layout Plans:
These plans show the placement of furniture within a room, often with scaled representations of sofas, chairs, tables, and beds. Dimensions are used to ensure that furniture fits comfortably within the space and allows for adequate circulation. These plans are particularly useful for interior designers and homeowners planning the layout of their living spaces. *Electrical Plans:
These plans indicate the location of electrical outlets, switches, lighting fixtures, and wiring. Dimensions are used to ensure that electrical components are placed according to code and are accessible for maintenance. Electrical plans are crucial for electricians and electrical contractors. *Plumbing Plans:
These plans show the location of pipes, fixtures, and drains. Dimensions are used to ensure that plumbing systems are installed correctly and comply with building codes. Plumbing plans are essential for plumbers and plumbing contractors. *As-Built Plans:
These plans document the final configuration of a building after construction is complete. They reflect any changes or modifications made during the construction process. As-built plans are crucial for future renovations, maintenance, and repairs.Each type of floor plan utilizes dimensions in a unique way, tailored to its specific purpose. Detailed floor plans for construction will feature comprehensive measurements and specific material callouts. Conversely, a conceptual floor plan might prioritize room adjacencies and overall spatial flow with less emphasis on precise measurements, focusing on relative proportions instead.
Analyzing Sample Floor Plans With Dimensions: Case Studies
Examining specific examples of floor plans with dimensions can illustrate their practical applications and highlight key design considerations. The following scenarios are presented to demonstrate diverse applications of floor plans and their dimensional representations.
*Small Apartment Layout:
A floor plan for a small apartment (e.g., 500-600 square feet) typically focuses on maximizing space efficiency. Dimensions are crucial for selecting appropriately sized furniture and appliances. The plan might show a combined living and dining area, a small kitchen, a bedroom, and a bathroom. Dimensions are used to ensure that there is adequate space for circulation and that furniture does not obstruct doorways or windows. Consider a studio apartment where the bed may be tucked away during the day to free up common space. Precise measurements are needed to accommodate furniture pieces that serve multiple functions. *Single-Family Home:
A floor plan for a single-family home (e.g., 2,000-3,000 square feet) is more complex, with multiple bedrooms, bathrooms, a kitchen, a living room, a dining room, and possibly a home office or a basement. Dimensions are used to define the size and shape of each room, as well as the placement of windows, doors, and closets. The plan might also show the location of staircases, hallways, and mechanical systems. Dimensioned plans for these homes will include both interior and exterior dimensions, property line setbacks, and overall square footage. Zoning regulations heavily rely on accurate dimensions within the floor plan. *Commercial Office Space:
A floor plan for commercial office space (e.g., 5,000-10,000 square feet) needs to accommodate a variety of functions, including individual workstations, meeting rooms, conference rooms, and common areas. Dimensions are used to ensure that each space is appropriately sized and that there is adequate circulation for employees and visitors. The plan might also show the location of electrical outlets, data ports, and HVAC systems. The dimensioned layout must adhere to accessibility guidelines (ADA) providing sufficient clearances and turning radiuses to accommodate wheelchairs effectively. The placement of fire exits and emergency equipment is also crucial and dimensionally defined on the plan. *Retail Store Layout:
Floor plans for retail spaces prioritize maximizing sales floor space and creating an efficient customer flow. Dimensions are used to plan the placement of aisles, display fixtures, checkout counters, and fitting rooms. The plan also needs to consider accessibility requirements and security measures, such as placement of security cameras and fire exits. Dimensions are key to optimizing the shopping experience and increasing sales.In each of these cases, the dimensions on the floor plan are not merely lines on a page; they represent tangible spatial constraints and opportunities. Careful consideration of dimensions is essential for creating functional, efficient, and aesthetically pleasing spaces.
Tools and Technologies Used in Creating Floor Plans With Dimensions
The creation of floor plans with accurate dimensions relies on a combination of tools and technologies, ranging from traditional hand-drawing techniques to sophisticated computer-aided design (CAD) software and Building Information Modeling (BIM) platforms.
*Traditional Hand-Drawing:
While less common today for professional use, hand-drawing remains a valuable skill for sketching initial concepts and annotating existing plans. Tools such as pencils, rulers, scales, and protractors are used to create scaled drawings with accurate dimensions. This method provides a tactile understanding of spatial relationships and is often used in the early stages of design. *CAD Software:
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software, such as AutoCAD, is widely used by architects, engineers, and designers to create detailed 2D and 3D floor plans. CAD software allows for precise dimensional control, easy modification, and integration with other design tools. It also facilitates the creation of construction documents and permit sets. CAD software offers tools specifically designed for dimensioning, allowing users to easily add linear, angular, and radial dimensions to their drawings. *BIM Software:
Building Information Modeling (BIM) software, such as Revit and ArchiCAD, takes floor plan creation to the next level by creating a digital representation of the entire building. BIM models contain not only geometric dimensions but also information about building materials, systems, and components. This allows for clash detection, energy analysis, and lifecycle cost analysis. BIM software automatically generates floor plans, elevations, and sections from the 3D model, ensuring consistency and accuracy across all views. *Laser Measuring Tools:
Laser distance measurers and laser scanners are used to accurately measure existing spaces and create as-built drawings. These tools can quickly and accurately capture dimensions, eliminating the need for manual tape measuring. Laser scanners create point clouds of the space, which can then be imported into CAD or BIM software to generate a 3D model. *Mobile Apps:
Several mobile apps are now available for creating simple floor plans with dimensions using a smartphone or tablet. These apps often use augmented reality (AR) technology to measure spaces and create a basic floor plan. While not as precise as CAD or BIM software, these apps are useful for quick measurements and preliminary space planning.The choice of tools and technologies depends on the complexity of the project, the required level of accuracy, and the budget. For small residential projects, CAD software may be sufficient. For large commercial or institutional projects, BIM software is often preferred for its comprehensive modeling capabilities.

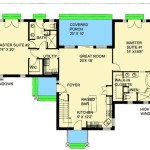
12 Examples Of Floor Plans With Dimensions

12 Examples Of Floor Plans With Dimensions

12 Examples Of Floor Plans With Dimensions

Small House Floor Plan With Dimensions Template

12 Examples Of Floor Plans With Dimensions

Sample Floor Plan Image With The Specification Of Diffe Room Sizes Scientific Diagram

Floor Plans With Dimensions Including Examples Cedreo

Features Create Floor Plan With Dimensions Room

How To Read A Floor Plan With Dimensions Houseplans Blog Com

Floor Plans With Dimensions Including Examples Cedreo
See Also